Green Building Techniques: A Guide to Sustainable Rural Living
Introduction:
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in green building techniques as people become more aware of the environmental impact of traditional construction methods. Green building not only helps reduce our carbon footprint but also promotes healthier living environments and lowers energy costs. For those embracing a rural lifestyle or homesteading, integrating sustainable practices into their homes is essential. In this article, we will explore various green building techniques that are particularly well-suited for rural living.
Passive Solar Design:
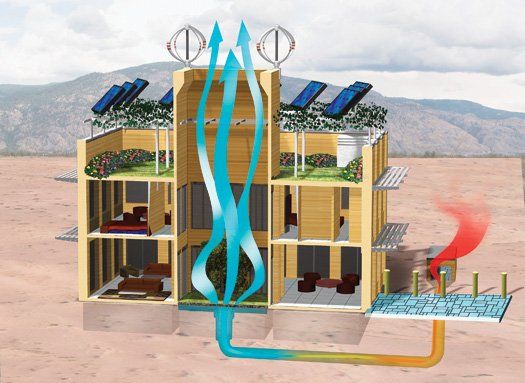
One of the fundamental principles of green building is harnessing natural resources like sunlight and airflow to minimize reliance on mechanical systems. Passive solar design takes advantage of the sun’s energy for heating and cooling purposes, reducing the need for artificial sources.
When designing or renovating your rural home, consider incorporating passive solar features such as large south-facing windows to maximize winter sunlight exposure while providing shade during hot summer months using overhangs or deciduous trees. Thermal mass materials like concrete or stone can absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night, stabilizing indoor temperatures.
Rainwater Harvesting:
Rural areas often lack access to municipal water supplies, making rainwater harvesting an ideal solution for both potable and non-potable water needs. Capturing rainwater not only conserves precious groundwater but also reduces runoff that can lead to erosion and pollution.
To implement rainwater harvesting on your property, start by installing gutters and downspouts connected to storage tanks or cisterns located near your home. Filters should be used to remove debris before storing water for later use in irrigation systems or even household consumption with appropriate treatment methods.
Greywater Systems:
Another innovative technique that complements rainwater harvesting is utilizing greywater systems. Greywater refers to gently used wastewater from sinks, showers, washing machines, etc., which can be treated and reused rather than being wasted down drains.
Implementing greywater systems starts with separating greywater from blackwater (toilet waste) and directing it to a treatment system. This treated water can then be used for irrigation, flushing toilets, or even in washing machines. However, it’s crucial to use non-toxic cleaning products to avoid polluting the soil.
Natural Insulation:
Proper insulation is vital for reducing energy consumption and maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures year-round. Opting for natural insulation materials not only enhances energy efficiency but also minimizes exposure to harmful chemicals found in conventional insulating products.
Materials like sheep’s wool, cellulose made from recycled paper, hemp fiber, or straw bales are excellent choices for rural homes. These sustainable alternatives provide effective thermal performance while being renewable and biodegradable.
Off-Grid Energy Systems:
Living off-grid is an appealing aspect of rural living that aligns well with green building techniques. Generating your own energy through renewable sources allows you to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and utility companies while enjoying greater self-sufficiency.
Solar panels are the most common form of off-grid energy generation. Installing photovoltaic (PV) panels on rooftops or ground-mounted arrays can harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. Additionally, small-scale wind turbines or micro-hydro systems may be viable options depending on local conditions.
Permaculture Design:
Green building extends beyond the physical structure of a home; it also encompasses how we interact with our surrounding environment. Permaculture design principles offer holistic approaches to land use planning, gardening, and resource management that promote sustainability and resilience.
Incorporating permaculture concepts into your property involves creating food forests using native plants, implementing efficient irrigation systems like swales or rain gardens, practicing organic gardening methods without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, composting organic waste material onsite for nutrient-rich soil amendments—the list goes on!
Conclusion:
Green building techniques serve as a blueprint for sustainable rural living by minimizing ecological impact, reducing energy consumption, and fostering self-reliance. From passive solar design to permaculture principles, there are numerous strategies available for those seeking a greener lifestyle.
Whether you’re constructing a new rural home or renovating an existing one, incorporating these techniques can significantly improve your environmental footprint while enhancing the quality of life for both present and future generations. By embracing green building practices, we can create harmonious spaces that coexist with nature and contribute positively to our planet’s well-being.

Leave a comment