In recent years, there has been a growing interest in finding alternative heating methods that are not only efficient but also environmentally friendly. One such method gaining popularity is biomass heating, which utilizes organic matter to produce heat. This article will explore the environmental impact of biomass heating and shed light on its benefits and potential drawbacks.
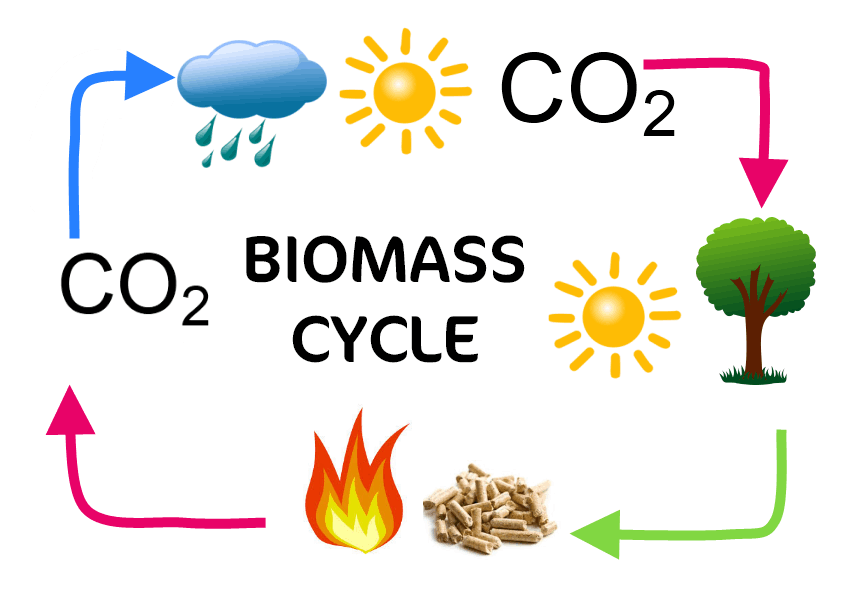
Biomass heating involves burning organic materials like wood pellets, agricultural residues, or dedicated energy crops to generate heat. Unlike fossil fuels such as coal or oil, biomass is considered a renewable energy source because it can be replenished through natural processes. Additionally, the carbon dioxide released during biomass combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth.
One of the significant environmental benefits of biomass heating is its lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based heating systems. While burning any material releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, using sustainably sourced biomass ensures that these emissions remain within ecological limits. In contrast, extracting and burning fossil fuels release ancient carbon stored for millions of years back into the atmosphere rapidly.
Moreover, when managed properly and with appropriate technology in place, modern biomass heating systems can significantly reduce other harmful pollutants associated with traditional wood-burning stoves or open fires. These pollutants include particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
Particulate matter can have detrimental effects on respiratory health when inhaled. Traditional wood-burning stoves often emit high levels of PM due to incomplete combustion or poor ventilation systems. Biomass boilers designed specifically for efficient combustion minimize these emissions through proper air supply control and advanced filtration systems.
Nitrogen oxides contribute to smog formation and acid rain when released into the atmosphere. However, modern biomass boilers use technologies like selective catalytic reduction or flue gas recirculation to reduce NOx emissions significantly.
Similarly, volatile organic compounds released during incomplete combustion can have adverse effects on air quality and human health. Biomass heating systems integrated with secondary combustion chambers or advanced gasification processes help minimize these emissions.
Sulfur dioxide emissions are primarily associated with the burning of fossil fuels like coal, which contains high sulfur content. As biomass does not contain sulfur in significant amounts, using it for heating purposes eliminates the release of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere entirely.
Furthermore, utilizing biomass as a renewable energy source can contribute to sustainable land management practices. Energy crops such as switchgrass or willow trees can be grown on marginal lands unsuitable for conventional agriculture. By cultivating these crops specifically for energy production, farmers can diversify their income streams while improving soil health and preventing erosion.
However, it is essential to address some potential drawbacks and concerns associated with biomass heating systems as well. The sourcing of biomass feedstock must be carefully managed to prevent deforestation or unsustainable logging practices. Clear cutting forests solely for their wood resources would have adverse environmental consequences by reducing biodiversity and disrupting ecosystems.
Additionally, transportation logistics play a crucial role in determining the overall carbon footprint of biomass heating systems. If long distances need to be covered to transport feedstock from its source to the end-user, this could offset some of the environmental benefits gained from using locally sourced materials.
Another consideration is ensuring that biomass boilers operate at peak efficiency levels throughout their lifespan. Regular maintenance and cleaning are necessary to prevent soot buildup or inefficiencies that can lead to higher emissions or reduced heat output.
In conclusion, biomass heating offers several environmental benefits when compared to traditional fossil fuel-based heating methods. It contributes significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and has the potential to reduce harmful pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides when modern technologies are employed correctly. However, it is vital that biomass sourcing is sustainable and properly managed while considering transportation logistics and ensuring efficient boiler operation over time. By addressing these challenges proactively, we can embrace biomass heating as a viable solution towards a greener and more sustainable future.

Leave a comment